The hands and fingers can make different movements owing to the presence of various bones. But how many bones in hand work together to function properly. The total number of bones in the hand as well as the wrist is twenty-seven. Among them, each little bone contributes towards the movements that your hands make.
Go through the description of how many bones in hand. Here you will also come across hand’s skeletal structure, interesting facts as well as the common bone disorders.
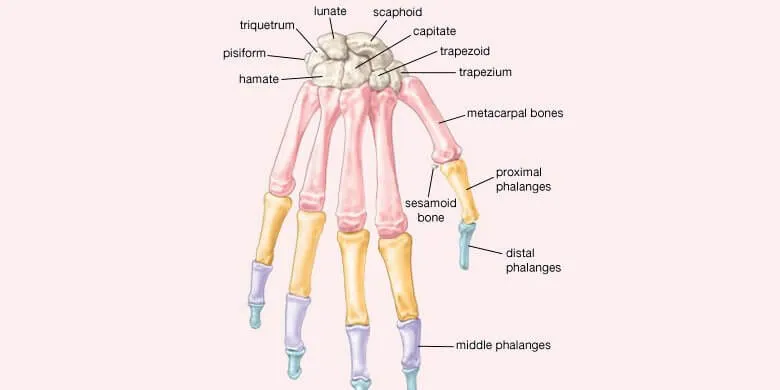
How Many Bones in Hand – Their Types:
After you have got basic information about how many bones in hand, it is time to learn about their types. The hand’s bones fall into two main types: metacarpal bones and phalanges. In addition, there is further division into smaller bones. A detailed description is as under.
Carpels
There are small carpal bones which make up your hand’s wrist – the carpus. They are eight in number and are irregular in shape. These bones have arrangement in two rows: distal and proximal. Each row consists of four bones. Their names are as follows.
Distal Row Carpels:
- Trapezium – a bone with four sides
- Trapezoid – a bone looking like a wedge in shape.
- Hamate – a wedge-shaped bone like the trapezoid. It also consists of a projection which you call as the hook of hamate.
- Capitate – the largest of the wrist bones. It has the same shape as the human head.
Proximal Row Carpels:
- Lunate – resembles a crescent moon in shape.
- Scaphoid – looks like a tiny boat in shape.
- Triquetrum – triangular in shape, like a pyramid.
- Pisiform – a small bone which is round in shape.
Metacarpal bones
The structure of the hand’s palm contains metacarpal bones. They are five in number. The palm has, therefore, also got the name, the metacarpus. The metacarpal bones do not have specific names. Instead, you can number them from 1 to 5. Each metacarpal consists of three main parts – base, shaft and head. Let’s discover more facts about how many bones in hand from the following discussion.
Phalanges
Concerning how many bones in hand, you should also consider phalanges. They are the bones of the fingers and the thumbs. The thumb phalanges have two parts – proximal phalanx and distal phalanx. On the other hand, each of the finger phalanges consists of three distinct parts – proximal phalanx, middle phalanx and distal phalanx.
Interesting Facts
Below are some intriguing facts about how many bones in hand.
- The hands and the feet contain half of the bones found in the entire body.
- The Latin word for moon is luna. This is what the crescent like carpel bone – lunate – has been named owing to its shape.
- The word scaphoid means boat-like. The boat shaped carpel – scaphoid – owes its particular name to its shape.
- An X-ray of the hand’s bones can reveal the approximate age of an individual. This plays an important part in forensic science and criminal case investigations.
- Wilhelm Rontgen carried out the first ever X-ray which was of the hand of his wife.
- Other than the regular hand and wrist bones, tiny bits of bone may form in the connective tissue which vary from one individual to another. Such a phenomenon has got the name of sesamoid bone variation.
- In scientific language, the bones of the thumb are referred to as the pollex while each of the fingers is called a ray.
- The bones of the hand enable various complex movements such as writing or playing a musical instrument.
- Since there are no muscles in the fingers, all the movements of the finger bones are operated through a “remote control”. The main control center is the brain. The muscles responsible for finger movement are in the palm and the mid forearm. These muscles make connections to the bones of the fingers through tendons.
- The bones of the fingers are straight at the back, but there is slight curvature at the side of the palm.
Disorders of the Hand Bones
While learning about how many bones in hand, you should also know about disorders of the band bones. The bones of the hands are a marvel in terms of their structural strength and ability to carry out complex movements. However, various disorders may impair their functionality. These disorders might occur in an old age, by accident or by birth. More detail is here below.
Nerve Compression Syndromes
This condition occurs when a bone or connective tissue presses a nerve. As a result, there is disturbance in the hand’s movement as well as pain in the region. Examples of nerve compression syndromes are:
- Carpel Tunnel Syndrome: It involves the compression of an important nerve passing over the carpel bones in the wrist. As a result, there is pain and movement problems in the hand and fingers.
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome – Cubital tunnel syndrome occurs due to compression of the ulnar nerve which passes through the elbow. It results in pain, tingling and numbness in the ring and pinky fingers as well as the forearm.
- Radial Nerve Syndrome – In this case, there is compression of the radial nerve at the elbow. It leads to pain and movement issues in the hand, fingers and the forearm.
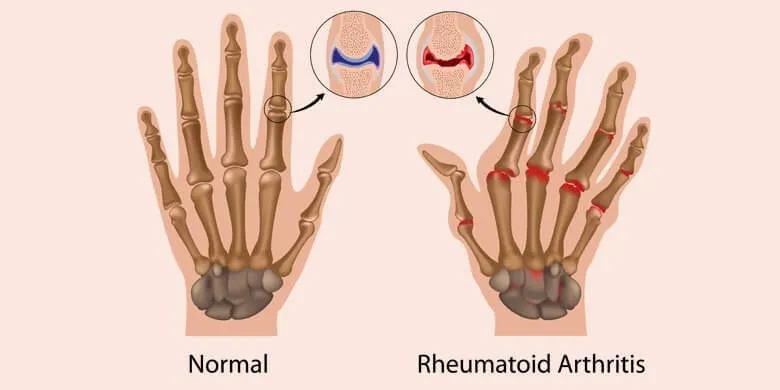
Deformities of the Hands and Fingers
Deformities may develop due to various reasons such as injury or other medical disorders like rheumatoid arthritis. Such deformities lead to several issues including pain and problems in the movement of the hand, wrist or fingers.
Kienbock’s Disease
When the blood supply to bones is inadequate, death of the bone tissue may occur. When the lunate bone – one of the carpal bones in the wrist – is affected due to this reason, it is the condition of Kienbock’s disease. It mostly affects individuals who have to do extensive manual labor. Men between the ages of 20 and 45 are likely to suffer from Kienbock’s disease.
Infections of the Hand and Fingers
Usually, the infections of the hand and fingers occurs animal bites. In this connection, the symptoms include abscess formation and constant pain. Doctors may prescribe antibiotics as a treatment for such infections.
Injuries and Fractures
Injuries of the bones occur by accident. However, sever injuries may lead to fractures which in turn vary in severity. For the sake their treatment, your healthcare provider can examine such fractures through X-ray of the bones.


