Names of 78 Organs of The Body (Educational)
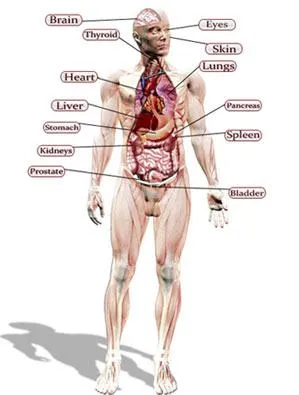
All the 78 (plus 2 newly discovered) organs of the body work in sync to form around a dozen organ systems. Made of billions of cells, each organ is assigned a single or several tasks.
Read on to unearth mysteries and discover intriguing aspects of the structure and function of the organs and their systems.
Here is the list of 80 organs.
- Adrenal Glands
- Anus
- Appendix
- Bladder
- Bones
- Bone Marrow
- Brain
- Bronchi
- Diaphragm
- Ears
- Esophagus
- Eyes
- Fallopian Tubes
- Gall Bladder
- Genitals
- Heart
- Hypothalamus
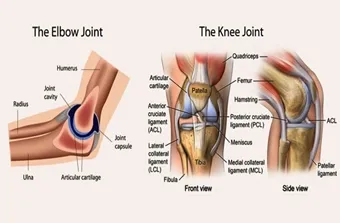
- Joints
- Kidneys
- Large Intestine
- Larynx (voice box)
- Liver
- Lungs
- Lymph Nodes
- Mammary Glands
- Mesentery
- Mouth
- Nasal Cavity
- Nose
- Ovary
- Pancreas
- Pineal Gland
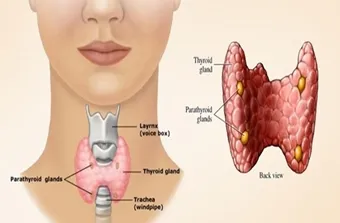
- Parathyroid Glands
- Pharynx
- Pituitary Gland
- Prostate
- Rectum
- Salivary Glands
- Skeletal Muscles
- Skin
- Small Intestine
- Spinal Cord
- Spleen
- Stomach
- Teeth
- Thymus Gland
- Thyroid
- Trachea
- Tongue
- Ureters
- Urethra
- Uterus
- Human skeleton
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Blood cells
- Vagina
- Vulva
- Clitoris
- Placenta
- Testes
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Seminal vesicles
- Bulbourethral glands
- Penis
- Scrotum
- Parathyroid glands
- Foramen Ovale
- Arteries
- Veins
- Capillaries
- Lymphatic vessel
- Tonsils
- Interstitium
- Nerves
- Subcutaneous tissue
- Olfactory epithelium
- Cerebellum
- 80th Organ
10 Largest Organs Of The Body
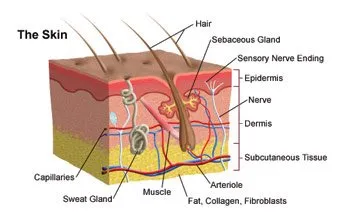
Skin
Do you really know or want to know, "What is skin?"...
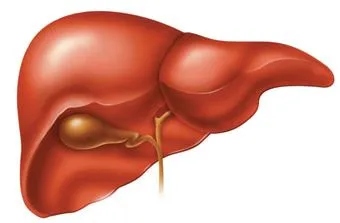
Liver
Do you know the secrets about the human liver...
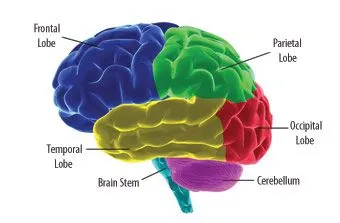
Human Brain
Did you know most of what you know about your brain has...
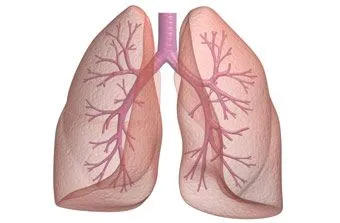
Lungs
Lungs are the major organ of our respiratory system...
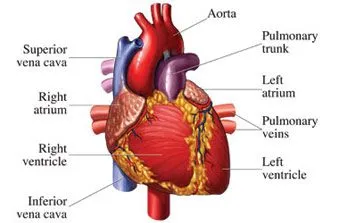
Heart
To understand the heart structure and function, you can...
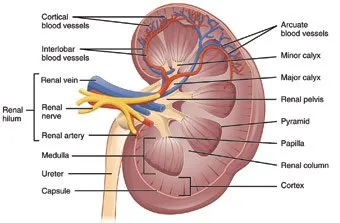
Kidneys
What Are Kidneys? Location Of Kidneys And Constituents...
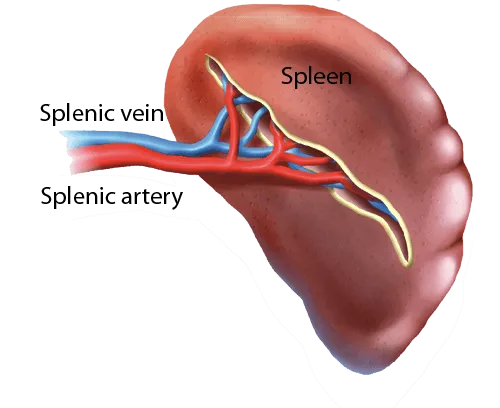
Spleen
The spleen can be defined as the largest gland of the...
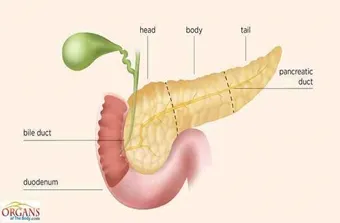
Pancreas
Some organs of the body serve as parts of more than...
Thyroid
Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland in adult...
Joints
You may logically assume that all the persons must have...
Organs and Organ Systems of the Human Body:
Do you know how the functions like communication, transportation, reproduction and growth are executed through the collective effort of different organs of the body? Though you would already be having a vast pool of information about your body, this article aims at revealing some stunning facts which may not be known to you.
In biology, a cell is known as the basic building block and the smallest unit of life. When similar cells combine into a group, they form a tissue. Two or more tissues, on the other hand, combine to form an important entity, called an organ. The grouping of different organs results in the formation of organ system.
There are as many as 80 organs which form groups and work in coordination with one another to accomplish a particular task. A group of organs assigned to complete a specific function, on the other hand, is called an organ system. For example, heart, blood, blood vessels and lungs are the major components of the blood circulatory system.
Do you know how many organ systems are there in your body? Well, there are nearly a dozen organ system, each made up of multiple individual organs working in coordination with one another. At the same time, there is coordination and linkage between different organ systems which combine to form an individual.
Among them, brain, heart, lungs, liver and kidneys are considered as the major or vital organs of the human body. The master organ, the brain, serves as CPU or control center, while beating of heart is considered as the sign of life in an individual.
The lungs assist in the supply of oxygen to every individual cell and the removal of carbon dioxide outside the body. The liver attaches with itself at least three superlative degrees, i.e. it is the largest, heaviest and hottest internal organ. Kidney serve as an important component of the excretory system which is responsible for the removal of the excess, unnecessary materials from the body fluids.
8 Major Organs of the Body:
All the organs of the body are not essential for the survival of an individual. There are certain organs, like arms, legs, stomach, large intestine, and tongue the complete removal of which will not put your life at risk. The other organs, like brain, heart, kidney, lungs and pancreas, etc. are indispensable for your survival. They are called the major or vital organs of your body. You can have a bird eye view of the shape, size and functioning of the major body organs through the following description:
- The Master Organ:
- The Pumping Organ:
- The Respiratory Organ:
- Dual-Functioning Glandular Organ:
- The Filtration Organ:
- The Detoxifying Organ:
- The Vision Organ:
- The Organ of Food Absorption:
Lying on the top of the body and enclosed in an incredibly hard protective cover of skull, the brain serves as the control center for all the functions of the body. Nearly 1.4-kilogram mass of brain occupies over 1200 cubic centimeter of space and accounts for about two percent of the total body weight.
Just like the brain of other mammalian species, it is distinguishable into three basic divisions of forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain. In absolute terms, the human brain is smaller than those of large mammals, like whales and elephants. But, when you take into account the measure of relative brain size, it happens to be twice as large as that of the bottlenose dolphin.
One of the most vital organs in the body, the heart is assigned the role of pumping blood with such a force that it reaches every individual cell. The blood carries with it nutrients as well as oxygen which are to be delivered to all the cells. Another important function of blood is to transport waste substances and gases for elimination out of body.
Measuring 5 inches in length, 3.5 inches in width and 2.5 inches in thickness, the human heart appears to be the size of a fist. However, an athlete’s pumping organ may grow much larger in size due to excessive exercise. There are four chambers in it, with the upper two being atria and the lower ones termed as ventricles.
Lungs are the respiratory organs as they are involved in the exchange of gases. If these vital organs are removed due to some disease, the affected person won’t be able to live anymore. They are found in the chest region on either side of the heart. The major tubular branches are called bronchi which gradually divide into bronchioles and alveoli – the smallest air sacs with single cell lining.
The primary role assigned to them is the extraction of oxygen from the atmospheric air and release carbon dioxide from the body. As you inhale air into lungs, oxygen is transferred to the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide in the bloodstream is transferred to the atmosphere.
Located behind the stomach in the abdominal cavity, the pancreas is a glandular organ. Owing to its dual-functionality, it is the closely associated with both the digestive system and endocrine system. This six-inch large organ can be distinguished into body, tail, neck and head.
Looking at its digestive function, the pancreas secretes and releases an enzyme-containing fluid into duodenum of small intestine, called pancreatic juice. It is known as an exocrine secretion. These enzymes help in the digestion of lipids, proteins and fats. The endocrine secretion of the organ contains some very important hormone, including insulin and glucagon.
The liver, kidney and lungs are the organs that purify blood. The enzymes secreted by liver detoxify various harmful substances and lungs eliminate carbon dioxide (a waste respiratory gas) from the blood. The kidneys, on the other hand, serve as the natural purifiers of your body.
Located in the back of abdomen, there are two bean-shaped kidneys with each measuring five or six inches in length. Their primary function is to filter waste substances from the blood and eliminate the same out of the body in the form of urine.
Metabolically, liver is the most complex organ in humans as it is assigned to form a number of different metabolically important functions. In addition to detoxifying poisonous substances, it also manufactures proteins and hormones. Other functions of the liver include blood clotting, control of blood sugar and killing germs.
As a detoxifier, the liver transforms various harmful substances like ammonia, metabolic wastes, alcohol and chemicals, into less harmful compounds. These neutralized and less harmful substances are then excreted out of the body.
Though not included in the list of vital organs, your eye makes you able to enjoy the soothing and fascinating colors of natural and artificial worlds around you. This complex organ has the potential to detect a single photon as well as distinguish nearly ten million colors!
The structure of eye can be distinguished into a small corneal segment and a large sclerotic chamber, measuring in 8 mm and 24 mm, respectively. Typically, an adult human eye may measure up to 7.5 gram in weight and six cubic centimeters in volume.
An integral component of the digestive system, the small bowel or small intestine serves as the major organ of food absorption. At the same time, it also plays an important role in the process of digestion. All the major types of food, namely, carbohydrates, lipids and proteins, are further digested and broken down into smaller absorbable products.
The small intestine is a bit longer in human females. It runs for the length of 6.9m and 7.1m in an adult male and female, respectively. It can have the diameter of up to 1 inch or a bit more. Interestingly, the total surface area can be as large as 30 square meters! But how is it possible? Well, these are the folds, villi and microvilli which significantly contribute to the enlargement of the surface area.
30 Interesting Body Organs Facts:
- The master organ brain is the control center of the body, acting just like CPU of a computer.
- Your liver is not only the hottest but also the largest and metabolically most complex internal organ of your body.
- With 60% of the dry weight contributed by fats, the brain happens to be the fattiest organ.
- The skin is the largest body organ which stretches across an area of 2 square meters and accounts for approximately fifteen percent of the body weight.
- The only organs of your body that can float on water are the lungs as they can hold nearly a liter of air at any moment.
- If all the airways running through the lungs are joined end to end, they can go up to the length of 2,400 kilometers!
- The rapid progress in the field of neuroscience has turned many of the ‘brain facts’ of past into ‘brain myths’ of today.
- Though human beings have been struggling to explore the secret power of brain for centuries, it still remains the least explored human body organ.
- Though accounting for just 2% of weight, the master organ utilizes around 20% of the total oxygen as well as energy required by the body.
- If taken out and joined end to end in a straight line, the blood vessels present in the skin can measure as long as eleven miles.
- Do you know that your memory, attention and other cognitive skills can severely be affected with just two percent dehydration of gray matter in the skull?
- Listed among the fundamental organs, the kidneys play the role of purification of blood and elimination of waste products through excretion.
- A kidney measures roughly the size of a computer mouse and, amazingly, if just 75% of a single kidney is functional, it can support life!
- Among organ transplants, the kidney transplant is very common. You can easily donate one of your kidneys without putting your life at risk.
- Known as the muscular hydrostat, tongue is the only muscle in the body that works without the support of skeleton.
- There can be as many as 10,000 taste buds found in your mouth, the majority of which are found on tongue and the remainder on lips, roof of mouth and cheeks.
- The total number of tiny air sacks, called alveoli, can be up to 500 million in both the lungs.
- Did you know that your fingertips are more sensitive than eyes as they contain a large number of receptors to send messages to the brain?
- The nails present on your fingers and toes are, in fact, the modification of hair.
- The hydrochloric acid secreted inside the stomach is powerful enough to kill the germs that enter with food, thus acting as the first line of defense for the immune system.
- The small intestine measures around six meters in length and it assimilates approximately ninety percent of food that you eat.
- Though an important organ of the human body, the removal of stomach does not pose threat to one’s life. People have already survived and can live without it.
- In the average life span of a human being, the large intestine processes approximately fifty tons of food. Put it in another way, a person consumes around 50 tons of food in the entire life.
- Just like stomach, it can be removed completely without posing a threat to the life of the individual.
- Until the 19th century, people knew nothing about the real function of the little rubbery organ, called pancreas.
- Owing to its rubbery nature, the medical experts have been considering pancreas merely a shock absorber with no other significant role in the body.
- When the pancreatic hormones are released into the blood stream, it is termed as endocrine secretion. On the other hand, the process of emptying pancreatic juice into the duodenum of small intestine is called exocrine secretion.
- The thoracic cage is made up of twelve uniquely curved bones, having head, neck and shaft, that collectively serve to give shape to upper part of your body as well as protection to the vital body organs.
- While running, you make use of all the leg muscles, so it is regarded as the best exercise for legs.
- The development of eyes starts as early as just two weeks after the conception. Did you know that your eye is so complex that it has over two million working parts in it?